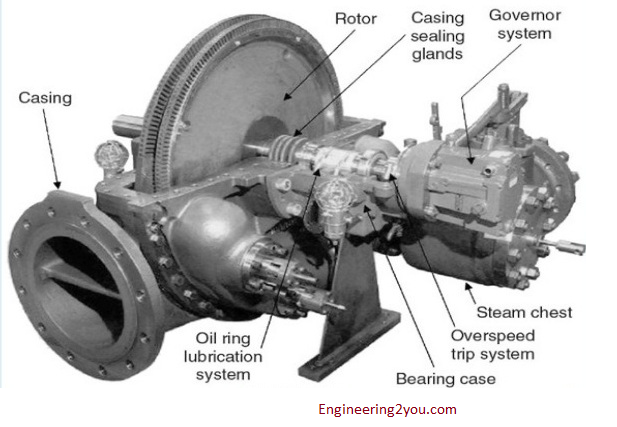
Basic Parts Of Steam Turbine
Turbine Casings
The casing form and construction details rely upon whether or not it’s a High Pressure(HP) or air mass (LP) casings. For low and moderate recess steam pressure up to one hundred twenty bar, one shell casing is employed. With an increase in recess pressure, the casing thickness is increasing.
Handling such serious casing is extremely troublesome conjointly the rotary engine on slowly remarked to the operation temperature. Otherwise undue internal stress or distortions to the thick casing could arise. To over this for prime pressure and temperature application double casing is employed. within the double casing inner casing is for prime pressure and also the outer casing is for hold the air mass.
Most of the rotary engine has casings with horizontal split sort. thanks to horizontal split it simple for collecting and dismantlement for maintenance of the rotary engine. Also, maintain correct axial and radial clearance between the rotor and stationary elements.
Usually, the rotary engine casings ar serious so as to resist the high pressures and temperatures. it generally follows the thickness of walls and flanges decrease from the recess to exhaust finish thanks to the decrease in steam pressure from recess to exhaust.
Turbine Casing MOC
Large casings for nonaggressive turbines are of welded plate construction, whereas smaller L. P. casings ar of forged iron, which can be used for temperatures up to 230°C.
Casings for intermediate pressures are typical of forged steel ready to stand up to up to 425°C. The high-temperature hard-hitting casings for temperatures surpassing 550°C ar of forged steel like three metallic element 1Mo (3% Cr + I Chronicles atomic number 42.)
The rotary engine casings are subjected to most temperatures and beneath constant pressure. therefore the fabric of casing shall subject high “Creep”. (Click here to browse a lot of regarding material properties)
The casing joints are fabricated from steam tight by matching the rim faces terribly precisely and really swimmingly, while not the utilization of gaskets. dowel pin pins ar wont to secure actual alignment of the casing rim joints.
The casing contains grooves for fixing the diaphragms (for impulse turbines) or for the stationary blades (reaction turbines). (Click here to browse a lot of regarding impulse and reaction turbines
Turbine Rotors
The {steam rotary engine|turbine} rotors should be designed with the foremost care because it is generally the extremely stressed part within the turbine. the look of a rotary engine rotor depends on the operational principle of the rotary engine.
The turbine, during which the pressure drops across the stationary blades. The stationary blades are mounted within the diaphragm and also the moving blades mounted or solid on the rotor. Steam escape is in between the stationary blades and also the rotor. The escape rate is controlled by labyrinth seals. This construction needs a disc rotor.
The turbine has pressure drops across the moving in addition to across the stationary blades. The disc rotor would produce an outsized axial thrust across every disc. therefore disc rotors aren’t utilized in the turbine.
For this application, a drum rotor is employed to eliminate the axial thrust caused by the discs, however not the axial thrust caused by the differential pressure across the moving blades. thanks to this, the configuration of the turbine is a lot of difficult.
Disc sort Rotors
This type of rotor is essentially utilized in steam turbines. The disc sort rotors ar created by shaping method. usually, the cast rotor weight is around five hundredths on top of the ultimate machined rotors. Refer on top of figure for disc sort rotor.
Drum sort Rotors
Initially, the reaction turbines rotors are created by the solid drum-type rotor. The rotors are serious and rigid construction. thanks to this, the inertia of the rotor is extremely high once compare with the disc-type rotor of constant capability. to beat this these days the hollow drum-type rotors are used rather than solid rigid rotors. Usually, this sort of rotor is created of 2 items construction. In some special cases, the rotor is created from multi-piece construction.
The drums are machined each outside and within to urge good rotor balance.
Turbine Blades
The potency of the rotary engine depends on over anything on the look of the rotary engine blades. The impulse blades should be designed to convert the mechanical energy of the steam into energy. constant goes for the reaction blades, that what is more should convert pressure energy to mechanical energy.
The blades are robust enough to resist the subsequent factors
- High temperatures and stresses thanks to the beating steam load
- Stress thanks to the force
- Erosion and corrosion resistance.
Depend upon the pressure region the blades are classified as follows. Refer on top of figure for rotor pressure region
- High Pressure (HP) blades
- Intermediate Pressure (IP) blades
- Low Pressure (LP) blades
The rotary engine blades are created from chromium-nickel steel or seventeen Cr’13 Ni – steel.
Stationary Blades (Diaphragms) and Nozzles
Nozzle:
Nozzles are wont to guide the steam to hit the moving blades and to convert the pressure energy into mechanical energy. within the case of tiny turbines, the nozzles are situated within the lower 1/2 the casing. however, within the case of the larger rotary engine, the nozzles are situated on the higher 1/2 the casing.
Stationary Blades (Diaphragms)
All stages following the management stage have the nozzles situated in diaphragms. The diaphragms are in halves and fitted into grooves within the casing. Anti-rotating pin or lockup items within the higher a part of the casing forestall the diaphragm to rotate.
All trendy diaphragms square measure of AN all-welded construction. The stationary blades in reaction turbines square measure fitted into grooves within the casing halves; keys as shown lock the blades in situ. In some cases, the blades have keys or serration on one aspect of the basis and a caulking strip on the opposite aspect of the basis is employed to tighten the blades solidly within the grooves.
Blade Fastening
After rotary engine blades square measure machined through the edge method. Then the blades square measure inserted within the rotor groove. rely on applying the blade root section varies
Blade roots square measure subject to require four styles of stress
- Tensile stress because of the centrifugal forces
- Bending stress because of fluid forces acting on the blade in the tangential direction
- Stress because of vibration forces.
Thermal stress conjointly because of the uneven heating of the blade root and also the rim.
Twisted Blades
This type of blades is employed within the last stage of an oversized time period turbine. These square measure the most important blade in the rotary engine and contribute around 100 percent of the rotary engine total output. because of larger in size, these styles of blades square measure subjected to high centrifugal and bending forces. to beat these forces twisted construction is employed.
Shrouds
Shrouds square measure accustomed reinforce the rotary engine blades free ends to cut back vibration and leak. this can be done by reverting a flat finish over the blades refer figure. In some cases particularly in the first stages, the shroud could also be integrated with the blade.
once the blades square measure terribly long as within the case of the last stage of record rotary engine. The rotor blades square measure any bolstered by mistreatment lacing wires (caulking wire) that circumferentially connects all the blades at a desired radius and shrouding is eliminated.
Turbine exclusion device
When a rotary engine is left cold and at standstill, the load of the rotor can tend to bend the rotor slightly. If left at the standstill whereas the rotary engine remains hot, the lower half the rotor can cool off quicker than the higher [*fr1] and also the rotor can bend upwards “hog”.
In each case, the rotary engine would be tough if not not possible to start out up. to beat the matter the manufacturer provides the larger rotary engines with a turning or exclusion gear consisting of an electrical motor that through many sets of reducing gears turns the turbine shaft at low speed.
The first turning gears turned the shaft at or so twenty revs/mm, later exaggerated to forty and up to sixty revs/mm as correct lubrication is tough to get at low speed; identical goes for the atomic number 1 seal of generators. Some turning gears, electrical or hydraulic, flip the shaft one 800 at set times over an amount of twenty-four hours.
Before a chilly rotary engine is started up it ought to air the exclusion gear for roughly 3 hours. once a rotary engine is finished off, it ought to be an exclusion for the future twenty-four hours. If an atomic number 1-cooled generator is concerned the rotary engine ought to be unbroken on exclusion gear to stop excessive loss of hydrogen, All exclusion gears square measure interlocked with a grease pressure switch ANd an engagement limit switch operated by the engagement handle.
Turbine Bearings
One of the turbine basic halves is bearing. they’re 2 styles of bearings used supported the kind of load act on them
- Radial Bearing
- Thrust Bearing
Radial Bearings
Steam Turbine Basic parts in the case of medium turbines used plain bearing. they’ll be ring greased sleeve bearings with bronze or Babbitt lining. each flooded and force sorts square measure used.
For larger turbines, the radial bearing is going to be a tilting pad kind. the amount of pad per bearing is going to be elect supported the load of the rotor. For these styles of bearing forced lubrication is employed.
Thrust Bearings
The main 2 functions of the bearing are:
- To keep the rotor in a certain position within the casing.
- To absorb axial thrust on the rotor because of the steam flow.
Steam Turbine Basic PartsThe bearing is found on the free finish of the rotor or we will say at the steam body of water of the rotary engine. The axial thrust force is extremely little for impulse turbines. this can be because of the presence of pressure-equalizing holes within the rotor discs to balance the thrust force generated across the disc.
An easy bearing like a bearing {for little|for little|for tiny} turbines and radial babbitt facing on journal bearings square measure usually utilized in small and medium-size turbines. cultivation pad kind thrust bearings square measure utilized in the big steam turbines.
In the case of the turbine, the pressure drop across the moving blades creates a significant axial thrust force within the direction of steam flow through the rotary engine. because of bigger thrust force, the serious duty bearing like tilting pad kind thrust bearings square measure used. The axial thrust in reaction turbines may be nearly reduced by the mistreatment off balance or dummy pistons.
As we tend to see the aim, the bearing not solely taking the thrust load and conjointly to take care of the position of the rotor. The axial position of the rotor is extremely necessary ANd an axial position indicator is commonly applied to the bearing.
As a standard follow, the axial position of the rotor exceeds zero.3 millimeter alarm and closing at zero.6 mm. (Readers please note these valves square measure thumb rule, it should amendment with reference to the manufacturer and rotary engine model)
Turbine Seals
Seals square measure wont to scale back the outpouring of steam between the rotary and stationary components of the turbine. rely on the placement of seal, the seals square measure classified as 2 varieties, they are
- Shaft Seal
- Blade Seal
Shaft Seals
Shaft seals square measure wont to stop the steam outpouring wherever the shafts extend through the casing. within the case of a tiny low rotary engine (as per API 611) carbon rings square measure used as shaft seal up to the surface speed of the shaft is 50m/s.
The carbon ring is formed from 3 segments butting along tightly beneath the pressure of a garter spring. The carbon rings square measure free-floating within the housing ANd an anti-rotating pin is employed to forestall the rotation of carbon ring seal.
Due to the self-lubrication properties of the carbon rings, they maintain a detailed clearance with the shaft. Refer below figure.
For larger steam turbines (as per API 612) labyrinth seal square measure used as shaft seals. within the case of compressing the turbine to forestall the air ingression at the shaft seal by secretory organ condenser and ejector arrangements(as per API 612).
Blade Seals
Blade seals square measure wont to stop the steam outpouring between the diaphragm and therefore the shaft. The potency of the rotary engine depends mostly on the blade seals. Labyrinth seals square measure used as blade seals within the little and huge turbines. within the case of huge turbine spring-loaded labyrinth seals square measure used.
The seals square measure created from brass or stainless steel. Also, the sharp edge offers higher protection and rubs off simply while not excessive heating just in case of a rather eccentric shaft. Some labyrinth seals square measure terribly straightforward, others square measure difficult.
Turbine Couplings
The purpose of couplings is to transmit power from the cause to the driven piece of machinery. versatile kind couplings square measure utilized in turbines. The coupling hubs square measure taper bore and key thanks to work the tapered finish of the shaft.
Governor
The governor is one of the turbine basic components. It is mainly operated is to regulate the operation of a turbine. Generally, the governor is assessed as 2 kind
- Speed-sensing governor
- Pressure sensing or load governor
Speed Sensing Governor
Speed-sensing governors square measure utilized in power generation application to keep up a continuing speed with relevance the load amendment in the governor. Droop is one of the vital characteristics of this governor’s choice.
Pressure-sensitive governor
These square measure applied to back pressure and extraction turbines in reference to the speed-sensitive governor.
They are 3 sorts of governor utilized in the turbine
- Mechanical Governor
- Hydro-mechanical Governor
- Electronic Governor
In the case of little rotary engine Oil relay kind (Hydro-mechanical) governor NEMA category “A” is employed. For the larger rotary engine, the electronic governor NEMA category “D” is employed.
Lubrication System
Oil flood lubrication is employed for tiny turbines and pressurized lubrication is employed for larger turbines. The pressurized lubrication system consists of a fill oil tank, oil pump, filter, cooler, pressure regulation valve, etc., The pressurized lubrication system of the rotary engine shall be as per API 614.






Post a Comment